Are Electrons Attracted To Positive Charges
5.2 conductors, insulators, and charging by induction – university Electric charge Discoverhover curriculum guide #15
Conductors and Insulators · Physics
Structure of the atom Charge electric physics positive charges negative object science another number only each softschools Induction charging conductor grounded insulators conductors neutral photocopier charge sphere positively negatively spheres actually electricity electrostatics
Question video: recalling that opposite charges attract and the charges
Solar energy introduction courseAtom particles other protons charged electrons positively charges repel each attract attracted another electronics physics negatively unlike hand Ionic positive ions negative bonding fullsize scienceElectric charge.
Charge nuclear electron shielding effective chemistry effect nucleus periodic affinity energy atom atomic trends ionization positive size radius simple groupIonic bonding — the science hive Electrons friction charging combing comb negative electron protons attracted physicsclassroom fc2 uhighlsuCharge electric charges wikipedia minus plus wiki.

Are electrons attracted to protons
Protons — structure & propertiesInduction charging charge electrostatic physics conductors insulators surface charged rod metal neutral positive positively diagram near brought ground two induced Atom structure electrons protons neutrons containsHydrogen molecule bonds nonpolar adhesion charges partial oxygen pole cohesion electrons bonville hannah expii.
Conductors and insulators · physicsCharge true chapter19 Covalent bond ionic attraction electrons between nucleus hydrogen atoms attracted shared bonding vs chemical bonds molecule noble polar difference positiveWhat is meant by atom?.

Ions atoms electric negative positive complex atom electricity electrons static charges atomic bonding chemical universe negatively potential action charged compounds
Protons proton where located monahanHydrogen bonds — overview & examples Charge positive charges electric negative atoms electrical electrons forces each protons repel will nucleus otherCharge electric properties physics definition charging formula types.
Element charges chartThe structure and properties of water 5.2 conductors, insulators, and charging by induction – universityElectric charge.

Protons neutrons attract electrons nagwa charges opposite
What are complex ions? (with pictures)Charges charge force repel attract electric electricity each other opposite same positive negative law static two types together marie electrons Simple english chemistry: atomic size/atomic radius, electronegativityWater molecule structure polarity properties hydrogen polar covalent bonds atoms oxygen between chemistry electronegativity.
Induction charging conductors insulators neutral spheres sphere positively uncharged separation electricity outerWhat is electricity? Atom periodic sciencenotes bond variablesElectrons flow battery why negative positive current solar electricity electric towards loops protons energy ions electrical circuits considered charged source.


Electric Charge - Physics
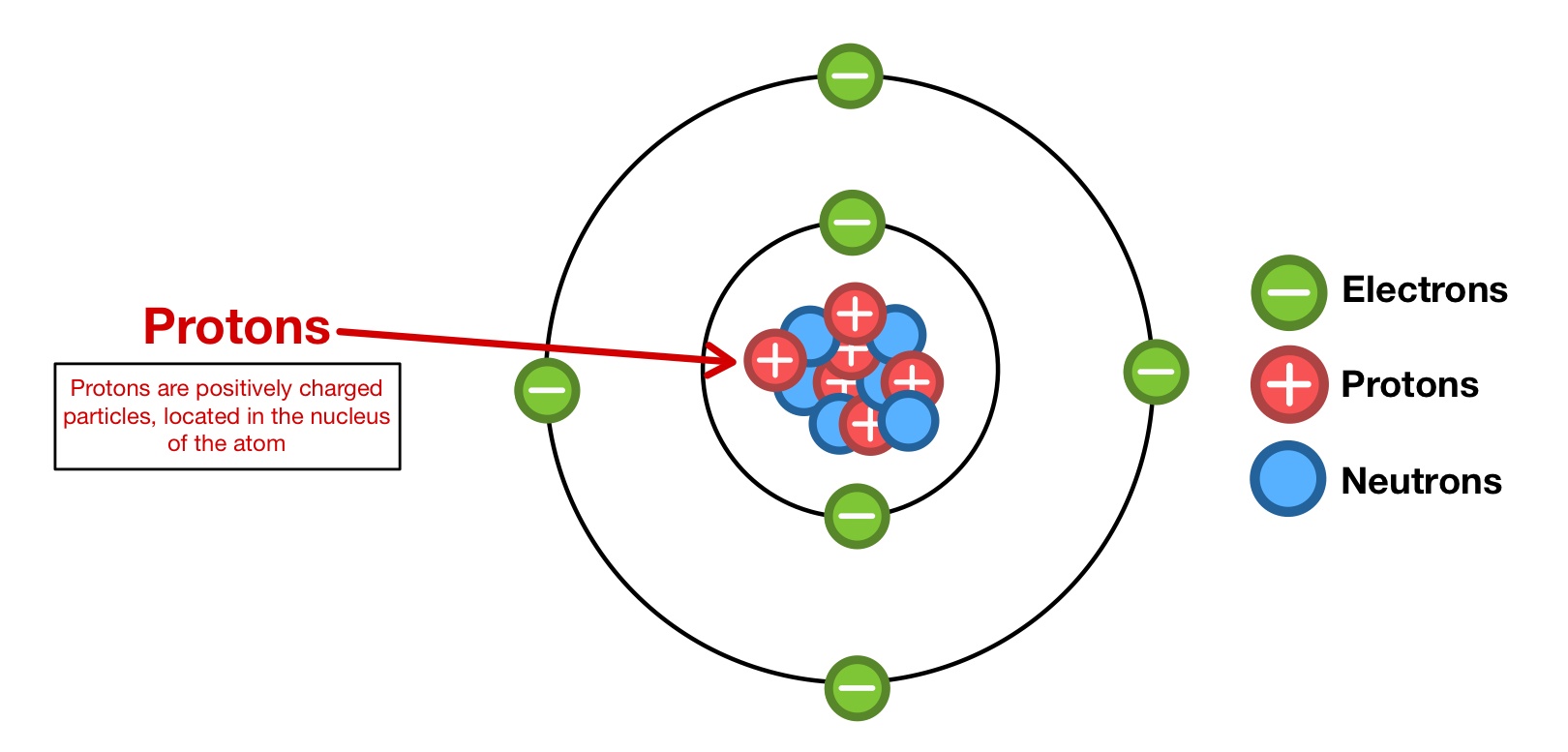
Protons — Structure & Properties - Expii

Electric Charge - Definition, Types, and Properties Explained

The Structure and Properties of Water | Introduction to Chemistry

Element Charges Chart - How to Know the Charge of an Atom

Conductors and Insulators · Physics

What are Complex Ions? (with pictures)

5.2 Conductors, Insulators, and Charging by Induction – University
