Representative Particles Can Only Be Atoms
Atoms elements molecules compounds mixtures chemistry science particle mixture compound matter physical vs models diagram school different table two worksheet Atoms structure particles subatomic three electrons protons neutrons which types spm there science Particles liquids solids gases primaryleap explorify tricky bits magnetix sl
SOLVED:Calculate the number of representative particles of each
Why study particle physics? Atoms molecules compounds nucleus difference electrons charged cloud positively surrounded whats consist negatively Particles atomic sub subatomic location ancient discoveries india scientific atom inventions amazing source
Lets get inside an atom!!
Representative particles, chemistry lectureArrangement of molecules in solid, liquid and gas Atoms protons neutrons electrons particle fundamental string quarks physics forces nature representation theory spark particles subatomic gif gluons do figureAtom atomic particles neutral atoms subatomic electrons protons electron destroyed byjus matter neutrons ion nucleus periodic.
What is matter? — definition & overviewMatter chemistry element substance pure compound atoms made ordinary shown classified 2.2 subatomic particles16 amazing scientific inventions and discoveries in ancient india.

Overview britannica
Particles subatomic atomic sub atom helium electrons charge labeled mass particle chemistry electron protons structure electric libretexts where discovered chemwikiAtom inside lets get Can an atom be destroyed?Covalent molecules compounds chemistry bonds molecular elements introduction.
Liquid solid molecules gas arrangement1b3 atoms and molecules Subatomic particlesWhat is matter?.

States of matter...tackle the tricky bits
Chapter quantities chemical particles representative ppt powerpoint presentation slideserveAtoms, molecules, and compounds: what's the difference? Particles subatomic atom atomic three definition discovery chemistry illustrated constitute primary belowCh150: chapter 4 – covalent bonds and molecular compounds – chemistry.
4.2 structure of atomsParticles atomic sub chemistry quantum nucleons completion target october date pages ppt powerpoint presentation slideserve Solved:calculate the number of representative particles of eachRepresentative number calculate particles each substance.


Atoms, Molecules, and Compounds: What's the Difference? | Owlcation
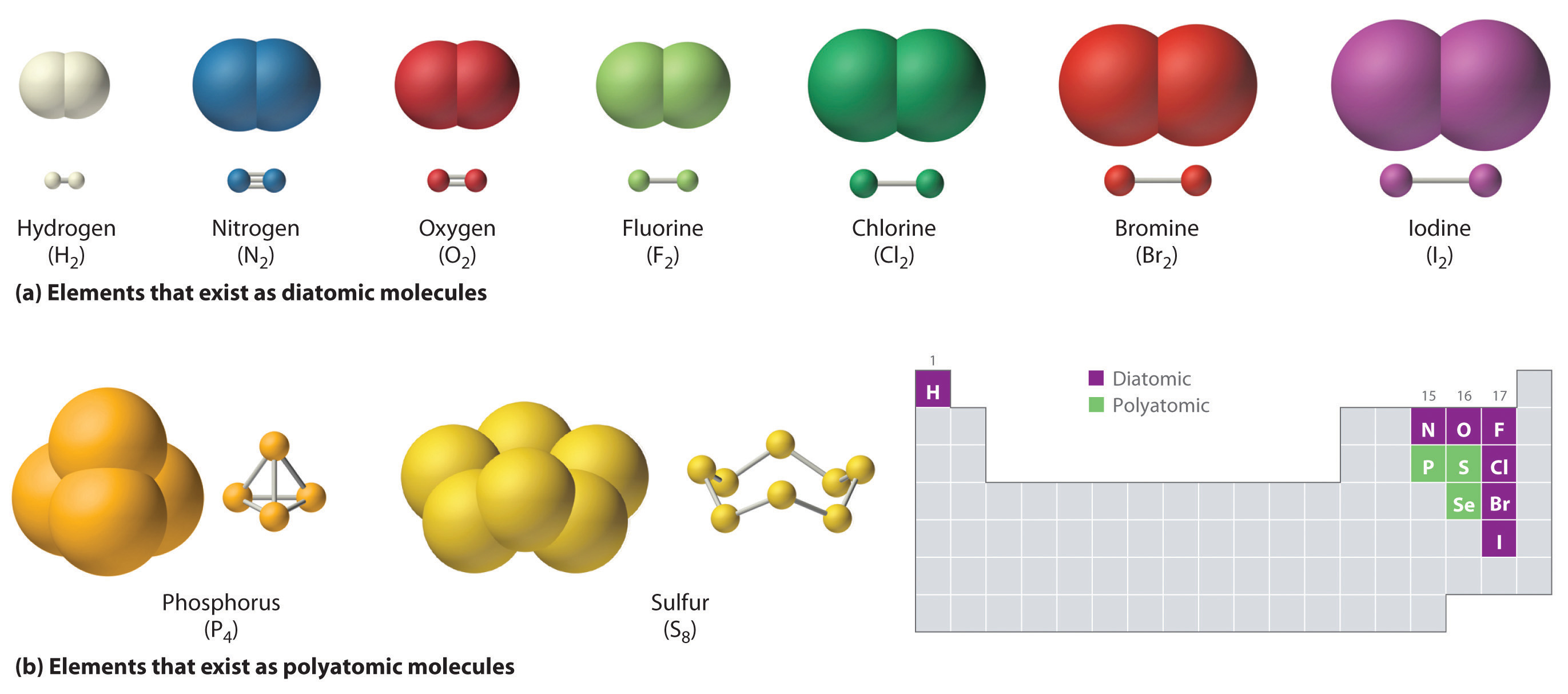
CH150: Chapter 4 – Covalent Bonds and Molecular Compounds – Chemistry
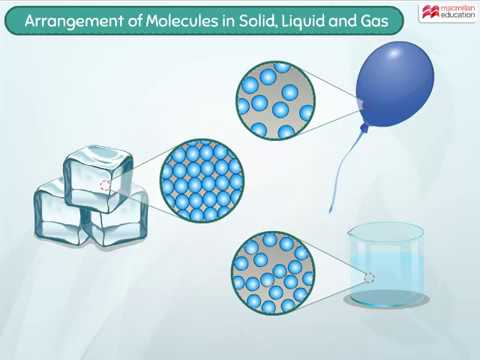
Arrangement of Molecules in Solid, Liquid and Gas | Macmillan Education

What is matter? - CHEMISTRY 9

What Is Matter? — Definition & Overview - Expii

Subatomic Particles - Definition, Discovery, and Key Features

Representative particles, Chemistry Lecture | Sabaq.pk - YouTube

4.2 Structure of Atoms - SPM Science

SOLVED:Calculate the number of representative particles of each
